Carbapenem-resistant IMP Detection K-Set (Lateral Flow Assay)
Product Introduction
The Carbapenem-resistant IMP Detection K-Set (Lateral Flow Assay) is an immunochromatographic test system intended for the qualitative detection of IMP-type carbapenemase in bacterial colonies. The assay is a prescription-use laboratory assay which can aid in the diagnosis of IMP-type carbapenem resistant strains.

Characteristics
|
Name |
Carbapenem-resistant IMP Detection K-Set (Lateral Flow Assay) |
|
Method |
Lateral Flow Assay |
|
Sample type |
Bacterial colonies |
|
Specification |
25 tests/kit |
|
Detection time |
10-15 min |
|
Detection objects |
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) |
|
Detection type |
IMP |
|
Stability |
The K-Set is stable for 2 years at 2°C-30°C |

Advantage
- Rapid
Obtain result within 15 min, 3 days earlier than traditional detection methods - Simple
Easy to use, ordinary laboratory staff can operate without training - Accurate
High sensitivity and specificity
Low detection limit: 0.20 ng/mL
Able to detect most of the common subtypes of IMP
- Intuitive result
There is no need for calculation, visual reading result - Economic
Product can be transported and stored at room temperature, reducing costs
The importance of CRE test
Collectively, Enterobacterales are the most common group of pathogens causing healthcare-associated infections. Some Enterobacterales can produce an enzyme called a carbapenemase that makes antibiotics like carbapenems, penicillins, and cephalosporins ineffective. For this reason, CRE have been called “nightmare bacteria” because there are few alternative antibiotics, if any, left to treat the infections caused by these germs.
Bacteria from the Enterobacterales family, including Klebsiella species and Escherichia coli, can produce a carbapenemase. Carbapenemases are often produced from genes located on transferable elements that can spread resistance easily from germ to germ and person to person. Also because of the abuse usage of antibiotics and limited methods taken to prevent spreading, the dramatically increasing CRE problem is becoming a life threat worldwide.
Usually, spread of CRE can be controlled by:
- Monitoring CRE infections
- Isolate patients with CRE
- Removing invasive medical devices inside the body
- Be careful when prescribing antibiotics (especially carbapenems)
- Using clean sterile techniques to minimize the spread of infection
- Strictly follow the lab cleaning routine
……
CRE detection is of great value in spread control. By testing early, health providers can give a more reasonable therapy to patients susceptible to CRE, also achieve the hospitalization management.
IMP-type carbapenemase
Carbapenemase refers to a type of β-lactamase that can at least significantly hydrolyze imipenem or meropenem, including A, B, D three types of enzymes classified by Ambler molecular structure. Among them, Class B are metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs), including carbapenemases such as IMP, VIM and NDM,. IMP-type carbapenemase, also known as imipenemase metallo-beta-lactamase producing CRE, is a very common kind of acquired MBLs and is from subclass 3A. It can hydrolyze almost all β-lactam antibiotics.
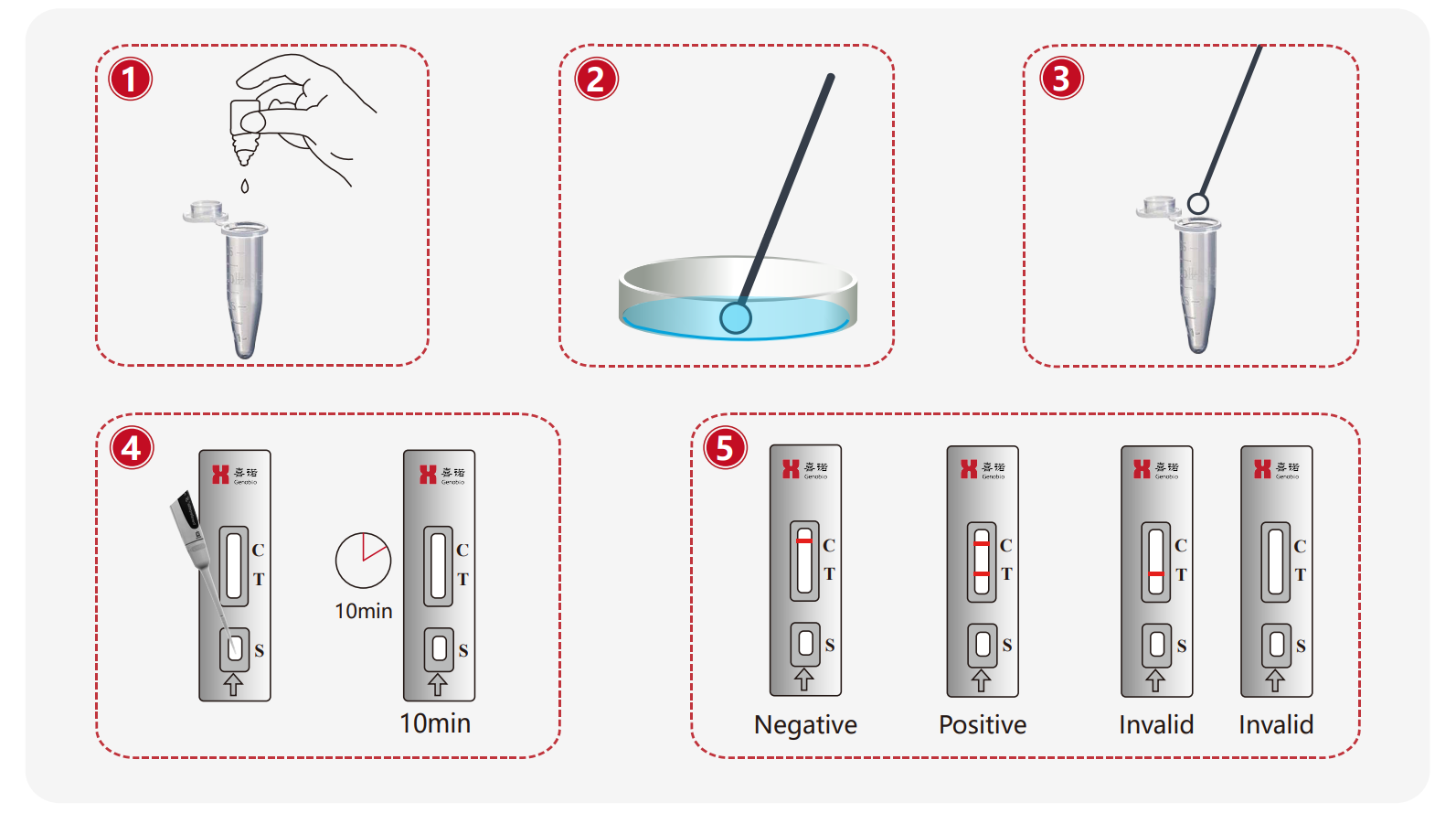
Operation
- Add 5 drops of sample treatment solution
- Dip bacterial colonies with a disposable inoculation loop
- Insert the loop into the tube
- Add 50 μL to the S well, wait for 10-15 minutes
- Read the result
Order Information
|
Model |
Description |
Product code |
|
CPI-01 |
25 tests/kit |
CPI-01 |